
Against this backdrop, it is necessary to take a proactive look at what could emerge as the new normal in the shipping and logistics industry in 2024 and how the industry will change in 2024.
According to the second half of 2023 forecast by UK shipping consultancy Clarksons[1], the ocean freight market is expected to grow by more than 3% in 2024. The global maritime and logistics market is growing rapidly due to high internet penetration and the expansion of e-commerce. In addition, the end of the COVID-19 pandemic era, which has adversely affected the shipping market, is expected to revitalize trade, making a positive impact on the shipping market.
On the other hand, in the coming year, digital transformation and decarbonization are expected to accelerate shipping market, and companies will become more active in increasing their competitiveness and seeking ways to respond to upcoming challenges. 1. Global Economy According to the International Monetary Fund's (IMF) July 2023 forecast, global real GDP growth in 2024 is expected to be 3.0%, the same as the 2023 forecast of 3.0%.
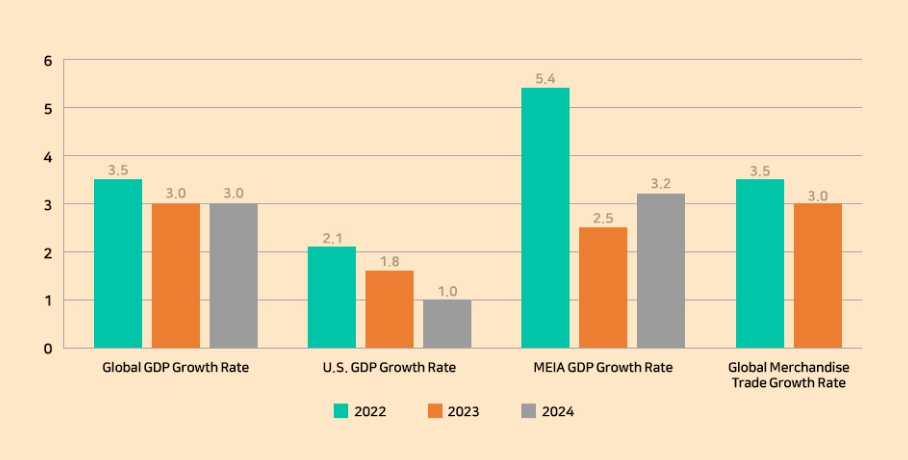 (Source: World Economic Outlook, IMF, July 2023) [2]
(Source: World Economic Outlook, IMF, July 2023) [2] The increase in global merchandise trade volume in 2024, which is expected to be more than 3 percent year-on-year, means that the global economy is recovering from the trade slowdown, thus revitalizing the global shipping and logistics market.
In October 2023, the IMF projected global inflation to reach 5.8% in 2024. This is an increase of 0.6% from the 5.2% global inflation forecast for 2024, which was made at the beginning of 2023. The IMF expects global inflation to remain elevated in 2024 due to high food prices, energy prices, and monetary tightening around the world, including in the United States.
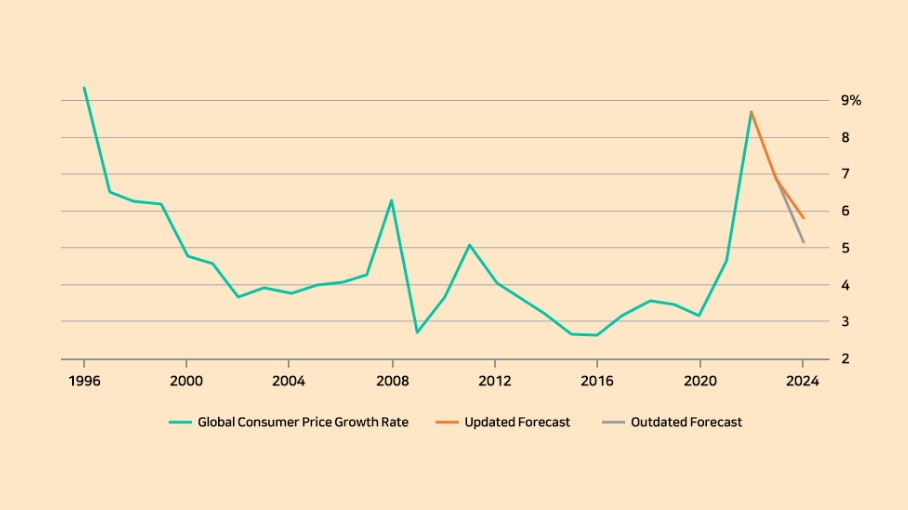 (Source: World Economic Outlook, IMF, October 2023) [3]
(Source: World Economic Outlook, IMF, October 2023) [3] However, global economic indicators released in November and December 2023 show that inflationary pressures around the world are easing somewhat, and U.S. government bond interest rates are trending downward from their high levels. In December 2022, Christopher Waller, one of the most prominent hawks at the U.S. Federal Reserve, stated that the central bank will cut interest rates in the future if inflation declines, and Chairman Powell confirmed that inflation is slowing, saying that the economy is showing signs of soft landing while balancing the risks of over-tightening and under-tightening.
If the high inflation and high interest rates that have persisted since the second half of 2024 are eased, consumption will likely be driven by real income growth, which will revitalize the shipping and logistics industry. 2. Rise of E-commerce The rise of e-commerce is driving the shipping and logistics market, a phenomenon that is expected to intensify in 2024.
According to Newscast, a Japanese logistics statistics provider, global retail e-commerce sales recorded $5,695 trillion in 2022, and global retail e-commerce sales are estimated to reach $6,542 trillion in 2023. E-commerce sales are expected to grow at an even faster rate in the coming years.
Online shopping is now one of the most popular online activities around the world, driving trade not only in emerging markets like China, India, and Indonesia, but also in developed countries like the U.S. and EU.
In the following figure, the green line represents the share of global e-commerce sales from emerging countries and the orange line represents the share of North American sales. E-commerce sales in emerging economies, such as China, India, and Indonesia, already accounted for 20% of total e-commerce transactions in 2022. North America, which includes the U.S., Canada, and other countries, accounted for 15.6% of total ecommerce sales in 2022. As such, global e-commerce trade is set to grow continuously even in 2024.
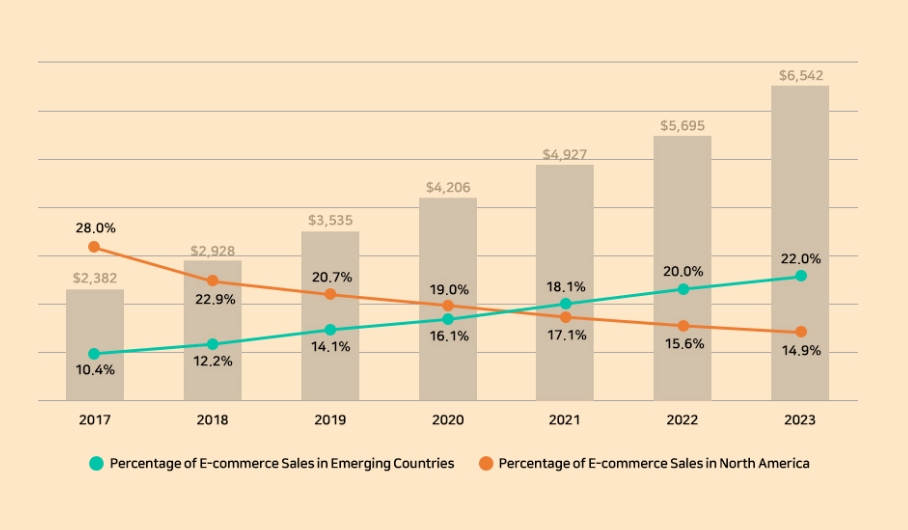 (Source: Newscast, July 2023) [4]
(Source: Newscast, July 2023) [4] In fact, the number of shipping and logistics companies linked to marketplaces is increasing, and shipping companies such as Maersk Line and Evergreen are providing services to transport goods ordered on e-Platforms such as Alibaba in China and Amazon in the U.S. by sea.
The e-commerce market will continue to expand in 2024 as non-face-to-face business is strengthened, and the proportion of goods shipped from e-commerce businesses is expected to gradually increase in shipping and logistics market. 3. Expansion of Digital Transformation In the post-COVID era of 2024, one of the key trends emerging in the shipping and logistics market is digital transformation. Digital transformation means freely collecting, sharing, analyzing, and disseminating large amounts of data in a secure way.
Digital transformation requires various technologies related to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, such as AI (including generative AI), cloud, and Internet of Things (IoT).
After the pandemic, the era of non-contact has arrived, and the competitiveness of the shipping and logistics industry is being determined by its digital transformation capabilities. The importance of digital transformation will continue to increase in 2024.
Through the implementation of digital transformation, the competitiveness of the shipping and logistics industry can be improved and the capabilities of shipping and logistics companies can be strengthened. Furthermore, shippers, who are consumers of transportation services, can transport cargo in a shorter period of time and at a lower cost, which ultimately leads to the sustainable growth of the global economy as well as the Korean economy.
As the “smart revolution” is coming to the shipping and logistics industry, digital transformation is expected to bring various benefits such as improved operational efficiency and enhanced safety operations.
The shipping and logistics industry, which accounts for more than 99% of Korea's imports and exports[5], surely has a huge impact on society as a whole, and the digital transformation of the shipping and logistics industry is highly necessary because it can contribute to the development of not only major players in the shipping and logistics industry, such as shipping lines and shippers, but also the national economy.
In summary, digital transformation is certainly a priority for the viability of the shipping and logistics industry in 2024. Optimizing fleet operations and promoting business continuity in digital will be a new survival strategy in the post-COVID era. Digital transformation is emerging as the new normal for shipping and logistics, and the level of digital transformation will determine the overall competitiveness of domestic and foreign shipping and logistics companies.
The following figure shows the changing trends occurring in the shipping industry with the advent of the digital transformation. For example, the acceleration of digital transformation has led to the increased usage of Industry 4.0 technologies, diversification of production bases, and an increase in non-face-to-face sales and non-face-to-face shipment booking. In addition, various other changes are witnessed, such as the establishment of a shipping and logistics platform that seeks to maximize efficiency due to the acceleration of digital transformation.
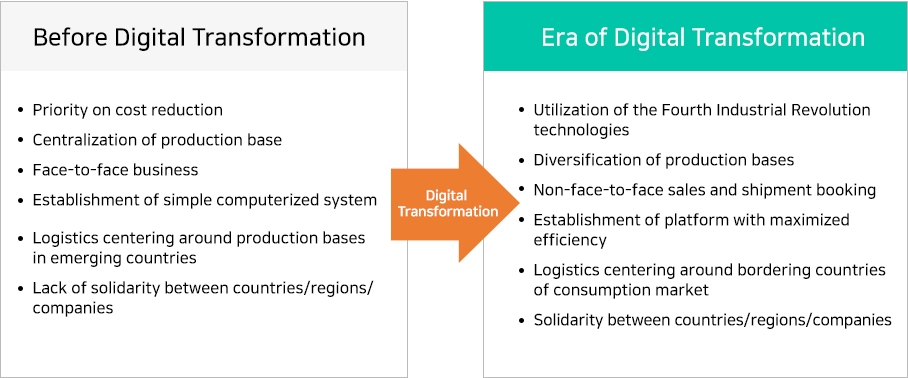 (Source: Author)
(Source: Author) The trend of decarbonization is accelerating more and more in the post-COVID-19 era. There are many movements to protect the environment and build an eco-friendly business ecosystem surrounding shipping and logistics market.
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) and other organizations have issued regulations related to decarbonization, such as establishing greenhouse gas reduction strategies to decarbonize shipping. According to the IMO, international shipping is required to reduce CO2 emissions per unit of transport work to achieve net-zero by 2050 compared to 2008. The decarbonization of the shipping industry is expected to accelerate through various regulations mandated by international organizations such as the IMO.
In fact, at the IMO's MEPC 80 (July 2023) meeting, it was decided that a combined measure of fuel oil standardization and greenhouse gas cost regulation would be nominated and its implementation measures would be further discussed.
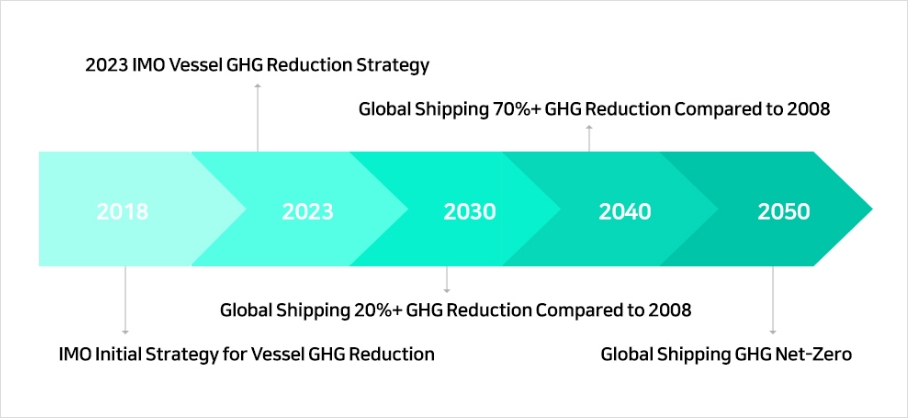 (Source: IMO) [6]
(Source: IMO) [6] For instance, according to the IMO's 12th Guideline on Greenhouse Gases published in May 2022, the annual carbon charge imposed on international shipping recorded around $80 billion (about 9.6 trillion won, assuming a KRW/dollar exchange rate of 1,200 won) at a rate of $100 per ton.
Considering that it usually takes more than two to three years for shipbuilding and delivery of a ship upon being ordered and the carbon charge will be imposed from 2027, one of the major topics facing the shipping and logistics industry in 2024 is decarbonization, which is why companies must make efforts to respond quickly and secure competitiveness.
Specifically, ammonia-powered ships, methanol-powered ships, hydrogen-powered ships, and electric-powered ships are emerging as the next generation of eco-friendly ships. In order to secure a leading position in the competition for the next generation of eco-friendly ships, the shipping and logistics market of each country will have to make continuous decarbonization efforts, such as driving R&D initiative.
 (Source : Getty Images Bank)
(Source : Getty Images Bank) First, with regard to digital transformation, the best way to strengthen competitiveness for industry stakeholders will be to promote business continuity, such as optimizing fleet operations digitally for carriers while enabling systematic and rapid order using digital technologies for shippers. In the wake of COVID-19 pandemic, shipping and logistics stakeholders are focusing on digital transformation more than ever before, and it is expected to become a common trend among shipping, logistics companies as well as shippers to drive strong digital transformation initiative.
Despite external factors such as the emergence of COVID-19, digital transformation is contributing to ensure that business processes run efficiently and without disruption. The core thrust of digital initiatives is to have a customer-centric mindset and provide flexibility for customers to use the business in any emergency. In such regard, it is necessary to strengthen efforts for digital transformation at the national level by establishing industry-academia-federal-government cooperation system on digital transformation.
Second, the development and deployment of zero-carbon ships is an attempt to promptly respond to customer needs. Shippers are increasingly choosing carriers that are willing to fulfill their social responsibilities through decarbonization, even if it means higher shipping costs. Regarding decarbonization, it is necessary to actively support the cooperation of relevant ministries so that each country can take the lead in the global decarbonization initiative by focusing on clean fuel research. Furthermore, reducing environmental pollutants through the implementation of decarbonization strategies will help the shipping and logistics industry fulfill its social responsibilities, and ultimately enhance its credibility at the national level by complying with international norms. # Reference [1] Clarkons, https://sin.clarksons.net/
[2] World Economic Outlook, IMF, 2023. 7.
[3] World Economic Outlook, IMF, 2023. 10.
[4] Newscast, https://newscast.jp/
[5] KOSIS, https://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=116&tblId=DT_MLTM_662
[6] IMO, https://www.imo.org/en/MediaCentre/HotTopics/Pages/Cutting-GHG-emissions.aspx
▶ This content is protected by the Copyright Act, and the copyright is held by the contributor.
▶ This content is prohibited from secondary processing and commercial use without prior consent.

